What Parts of the Brain Does What?
The brain
is one of the essential organs in the human body. Its complexities are varied,
making it a wonder among medical professionals and ordinary folk.
The brain is
considered to be the nerve centre of the body because it controls most of the activities
the body can do. It is a mass of nerves as well as support tissues that connect
to other major organs in the body.
Some of these activities are as simple as
blinking, walking, talking and hearing, eating, and even breathing. When the
brain is connected to organs such as the spinal cord and different nerves, it
is referred to as the central nervous system.
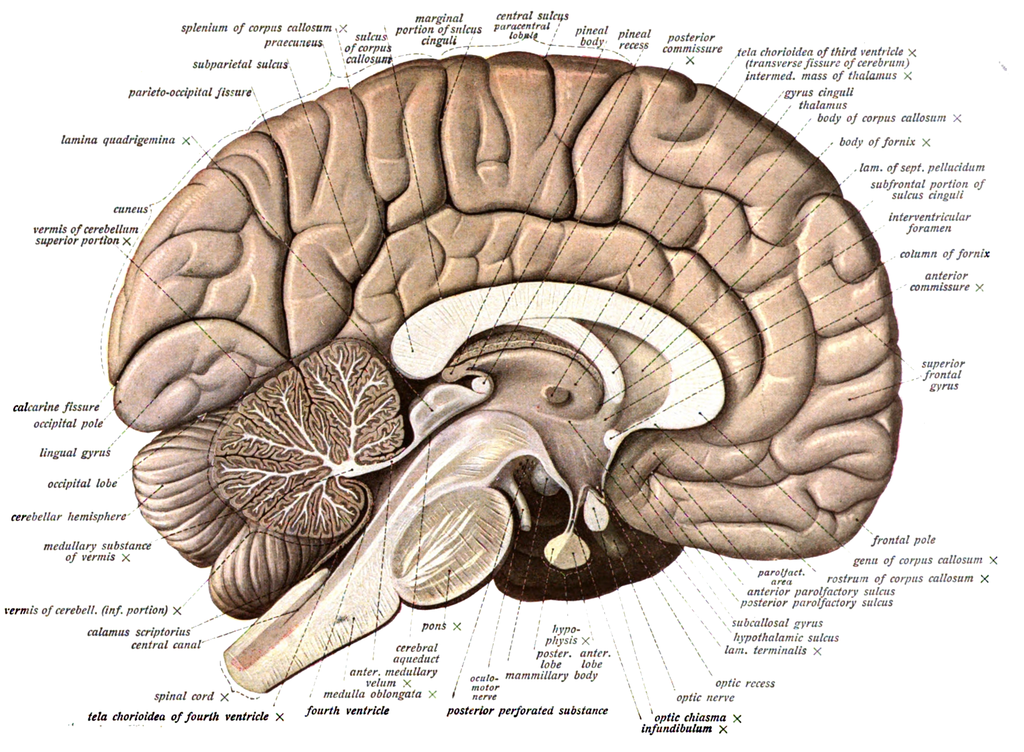
Structure of a
human brain
The
complexities of the human brain have been fascinating for medical professionals
that have been interacting with it for decades. Discoveries concerning its
structure have been mind-boggling and led to many breakthroughs in the medical
world.
Although the parts of the brain are many, some form its primary anatomy
while others are seen to serve supportive roles. It is common to see these
areas highlighted in a brain model labeled used in
educational institutions. Here are some of the significant parts of the organ
you need to know and what they do.
1.
Cerebral cortex
The part
of the brain that is seen when looking at its outermost portion is the cerebral
cortex. It is responsible for the many functions that make each human being
unique.
Some of the different traits observed in humans such as consciousness,
reasoning, higher thought and language come from that part of the brain. Also,
it comprises of four lobes that control different functions in the body. These
lobes include frontal, temporal, parietal and occipital lobe.
·
The Frontal lobe
is located in the anterior part of the brain and does many things such as
reasoning, expressive language and high-level intellect. The lobe also has a
motor cortex at the back which is responsible for receiving and utilizing
information from other sections of the brain. Information from different lobes
is then used to direct body movements.
·
The Temporal lobe is
at the bottom part of the brain and is host to the auditory cortex and
hippocampus. The auditory cortex is responsible for the understanding of languages
and sounds that we interact with daily. On the other hand, the hippocampus is
responsible for memories, how they are formed and kept in that part of the
brain.
·
The Parietal lobe is
at the middle of the brain and is associated with the processing of pain, touch
and pressure. The part of the brain also has the somatosensory cortex that is
responsible for the processing of various body senses.
·
The Occipital lobe
is found on the back part of the brain is tasked with interpretation of visual
information and stimuli. The section of the brain also hosts the central visual
cortex responsible for receiving information from the eyes and interpreting it
appropriately.
When it
comes to the functions that they control, these lobes or sections operate
individually as well as collectively to ensure the body works well.
2.
Cerebellum
The
cerebellum is an integral part of the brain and is located at the back of the
head, near the brain stem. In terms of size, this part of the brain occupies
ten percent of the entire organ and is home to at least fifty percent of its
neurons. It also comprises of tiny lobes that receive information from
different systems in the body.
These systems include visual, auditory, sensory
and the inner year. Some of the main functions of the body associated with the
cerebellum include controlling of balance, posture and voluntary movement coordination.
When the cerebellum is working well, it results in muscle groups working
together, resulting in fluid movement. Additionally, this part of the brain
plays a role in various cognitive functions such as speech.
3 Brain Stem
The stem
of the brain is the primary connection between the spinal code and cerebrum. It
is found at the bottom part of the organ and is made up of the medulla,
midbrain and pons.
·
The Medulla is
found on the top part of the spinal cord near the lowest part of the stem
within the brain. It controls different functions of the body, which are vital
such as blood pressure, heart rate and breathing.
·
The Midbrain works
as a relay station in the brain and is considered its smallest region. It controls various functions of the brain
like eye movement, visual as well as auditory information. The substansia nigra and red nucleus are the parts of the brain that
controls movements of the body. Dopamine producing neurons are found in the
substansia nigra, which is darkly pigmented.
·
The Pons primarily
connects the cerebrum, medulla and cerebral cortex. They play important roles
in the body that are often considered automatic. These roles include control of
sleep cycles and breathing which are essential to the functioning of the body.
4.
Thalamus and
hypothalamus
The Thalamus
and hypothalamus parts are essential for the proper functioning of the brain
and the entire body. They are located on the brain stem and the bottom of the
brain, respectively while performing various functions.
The thalamus is tasked
with the duty of collecting sensory information and transferring it to the
cerebral cortex, which then responds appropriately. The response sent back to
the thalamus is relayed to other body systems.
On the
other hand, the hypothalamus which is next to the pituitary gland also has its
unique functions in the body. These functions include controlling circadian
rhythms, hunger, body temperature, thirst and emotions. It also controls the
functioning of the pituitary gland, which involves secreting of essential
hormones in the body.
In
general, the brain is a critical organ in the body, and all its parts should be
protected at all costs. It is crucial to understand how it works for personal or
educational reasons to treat it well and prevent it from getting damaged in any
way.












Leave a Feedback